The presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. Cholesterol is a waxy substances that is produced by the liver and is a component of all cells found in the body. All of the cholesterol a person needs is produced in the liver, but another source is dietary cholesterol, which comes from animal food products such as meat, poultry, dairy, egg yolk and fish. Such foods are rich in saturated fats and trans fats, substances that can trigger the liver to make an excess of cholesterol and in some cases, this can lead to hypercholesterolemia
Cholesterol is required for various bodily functions including the synthesis of cell membranes and certain hormones and the production of substances required for fat digestion. However a cholesterol level that is too high increase the risk of CAD (Coronary artery disease)
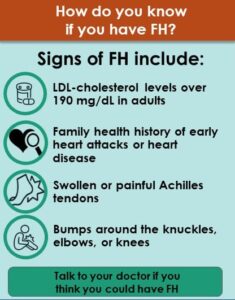
There are also inherited forms of hypercholesterolemia that can cause excess cholesterol to accumulate in other bodily tissues such as the tendons or under the skin of the eyelids. The most common cause of these conditions is familial hypercholesterolemia. Although high cholesterol level can be inherited, it is usually the result of a diet high in saturated fat and low level of physical activity. It can therefore often be prevented through healthy lifestyle choices such as exercising regularly and following a low-fat diet. If diet and exercise do not bring the cholesterol level down, cholesterol lowering medications may be recommended.
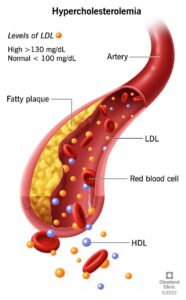
Cholesterol is circulated in the blood attached to transport proteins, a combination referred to as lipoproteins. These lipoproteins are classified depending on the type of cholesterol they carry. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carries cholesterol from the liver to various parts of the body. If there is an excess of LDL, cholesterol can accumulate in the walls of arteries and lead to atherosclerosis. LDL is therefore sometimes called “bad cholesterol.”
High-density lipoprotein (HDL), on the other hand, carries excess cholesterol away from cells to the liver, where it is broken down and treated as a waste product. This lipoprotein is referred to as “good cholesterol.”
Unhealthy lifestyle choices such as physical inactivity, a high-fat diet and obesity increase the risk of a high LDL level and a low HDL level. Other risk factors include, smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, and having a family history of stroke or heart disease.
CAUSES
Common causes of high cholesterol include:
- Eating a diet high in saturated fat and trans fat, often found in animal meat and processed foods.
- Eating foods high in cholesterol, such as red meat and full-fat dairy.
- Certain genetic changes can cause familial hypercholesterolemia. These changes make the body unable to get rid of excess cholesterol, causing it to build up in the blood.
- People with familial syndrome aren’t able to lower cholesterol through diet and exercise alone.
Other risk factors include:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Type 2 diabetes
- Age
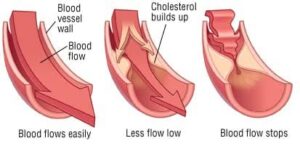
Excess cholesterol builds up in the bloodstream. It collects in the arteries, causing them to get clogged.This makes it harder for blood to flow normally through your body and can lead to heart disease, stroke, or heart attack.
Familial high cholesterol can lead to heart disease at a young age.
It can also cause deposits of cholesterol under the skin. These look like bumps that can show up around the eyelids or over the hands, knees, or ankles.

SYMPTOMS
In the early years there may be no symptoms.
Symptoms that may occur include:
- Fatty skin deposits called xanthomas over parts of the hands, elbows, knees, ankles and around the cornea of the eye
- Cholesterol deposits in the eyelids (xanthelasmas)
- Chest pain (angina) or other signs of coronary artery disease may be present at a young age
- Cramping of one or both calves when walking
- Sores on the toes that do not heal
- Sudden stroke-like symptoms such as trouble speaking, drooping on one side of the face, weakness of an arm or leg, and loss of balance.
DIET
Diet plays major role in fluctuation of cholesterol levels. Cut foods with high sugar, high sodium or increased saturated fats. Avoid Red meat, full fat dairy, egg yolk, deep fried foods like french fries, Peanut butter, oily foods, chocolates, White rice, White bread, baked foods, soft drinks etc.
Fishes like salmon, dry fruits like almond and walnut is rich in Omega 3 fatty acids may be helpful in protection against Cardiac ailments by reducing Triglyceride and cholesterol levels. Stick to veggies and fruits , nuts like walnuts, almonds, legumes etc.
Along with healthy diet and exercise there are herbs and medicines which are safe and effectively reduce the cholesterol naturally. According to Siddha herbs like Marutham (Terminalia arjuna), Garlic (Allium Sativum), Coriander (Coriandrum sativum), Curry leaves (Murraya koenigii), Turmeric (Curcuma longa), Kukkil or Guggulu (Commiphora wightii), Tulsi (Holy basil), Ginger (Zingiber officinale) etc are used in treatment of increased cholesterol levels.
EXERCISES
Brisk walking for 30 minutes or cardiac workouts 5 days a week helps to improve HDL and lower VLDL and Triglyceride and also helps to strengthen heart muscle.
Avoid Smoking and Alcohol :
Self analysing Cholesterol level. A simple blood test of Lipid Profile may help one check his or her Cholesterol levels time to time. This test should be performed at least once in a year or six months.
Drink plenty of water : Make sure to drink 6-8 glasses of water daily.
Lipid Profile
Total Cholesterol – Should be less than 200 mg/dl
LDL – Less than 100 mg/dl
HDL – Should be more than 40 mg/dl
Triglyceride – Should be less than 150 mg/dl
YOGA
- Kapalbhati pranayamam
- Chakrasana
- Shalabhasana
- Sarvangasana
- Paschimottanasana
- Ardha matsyendrasana



Greetings from Singapore
Sir i wish buy yr products
Can u share yr mobile number
Will call u
HELLO SIR,
WARM GREETING FROM AYUSH BUY.WE ARE GLAD TO SEE YOUR MESSAGE SIR, FOR FURTHER DETAILS PLEASE CONTACT: 6382282752
THANK YOU.